Also known as: ECG or electrocardiogram
Duration: About 10 to 20 minutes
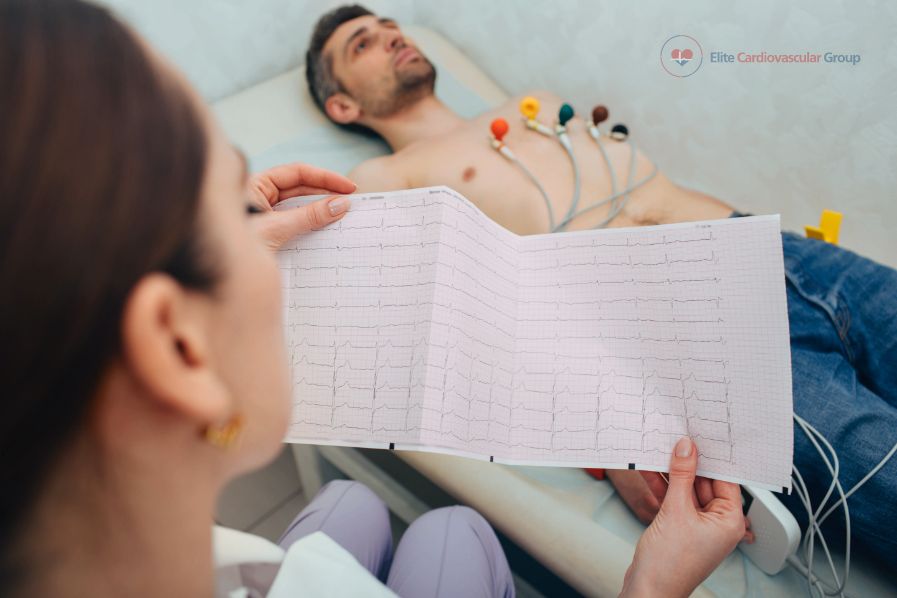
The EKG is a routine and painless test that is used to check the heart’s electrical activity. The EKG gives information about the heart rate, rhythm, heart’s shape, function of the valves, and general function.
Types of Continuous EKG Monitoring:
- Standard
- Continuous
Uses:
- To diagnose an active heart attack or to check a previous episode
- To diagnose irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias)
- To assess chest pain
- To check how well a pacemaker is working
- To check if certain medications are working properly
Preparing for the test:
![]() Download Pre Test Instructions
Download Pre Test Instructions
How it is performed:
- About 10 to 12 sticky electrode patches will be placed on your chest area and limbs.
- The electrodes will be connected by lead wires to an EKG monitor.
- The electric activity of the heart is recorded as “waves” and is displayed on the ECG monitor and/or printed on a strip of graph paper.
- Make sure you are comfortable when you lie down as movements of any kind might interfere with the results.
After the test:
- The technician will remove the electrode patches and you can continue with your regular activities.
- The results will be discussed by your cardiologist.
- Ask your cardiologist if you have any questions or concerns.
Show references
InformedHealth.org [Internet]. Cologne, Germany: Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG); 2006-. What is an electrocardiogram (ECG)? 2019 Jan 31. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536878/
Rogoff B, Pride YB. ECG (EKG) Rhythm. [Updated 2020 Mar 29]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK555952
