Also known as: ABI or exercise ABI
Duration: About 30 minutes
The ABI is a noninvasive, rapid test that can check for peripheral arterial disease (PAD) by measuring the blood pressures of your ankles and arms. The ABI can be compared before and after walking on a treadmill or riding on a stationary bicycle (known as exercise ABI) to evaluate the degree of stenosis/narrowings. If the ABI is low, it could be indicative of blocked or stenosed peripheral arteries.
Uses:
- To check for peripheral artery disease with symptoms (ex: leg pain while walking) or without symptoms
- If you have a history of diabetes, smoking (or tobacco use), high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis
- To follow up after surgery in the blood vessels of you your leg
- To evaluate the risk of future heart attack or stroke
Preparing for the test:
![]() Download Pre Test Instructions
Download Pre Test Instructions
How it is performed:
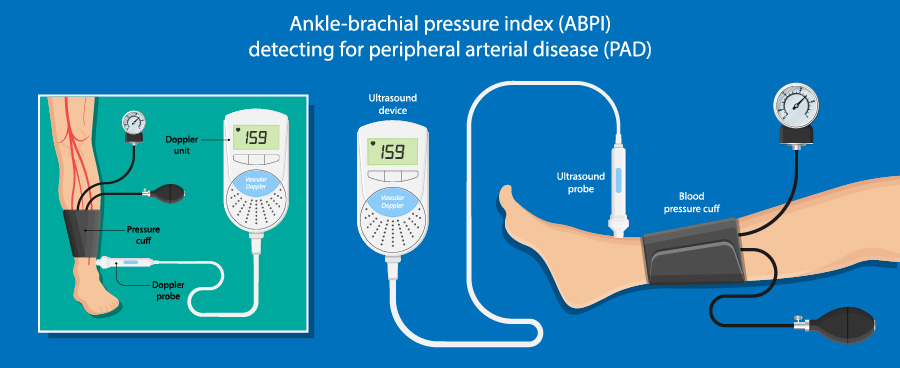
- Firstly, you are asked to lie down to relax for a few minutes.
- The resting blood pressures of both of your ankles and arms will be taken using an inflatable cuff; the readings will be compared in both sides of the body.
- An ultrasound probe will also be placed against your ankles and arms.
- Once the cuff is deflated, the ultrasound shows pictures of how well the blood flows in the arteries and the pulse can also be heard.
After the test:
- Your cardiologist will discuss the results with you.
- You can continue with your daily routine.
- Ask your cardiologist if you have any questions or concerns.
Show references
Rac-Albu M, Iliuta L, Guberna SM, Sinescu C. The role of ankle-brachial index for predicting peripheral arterial disease. Maedica (Bucur). 2014;9(3):295-302.
Khan TH, Farooqui FA, Niazi K. Critical review of the ankle brachial index. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2008;4(2):101-106. doi:10.2174/157340308784245810
Crawford F, Welch K, Andras A, Chappell FM. Ankle brachial index for the diagnosis of lower limb peripheral arterial disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016;9(9):CD010680. Published 2016 Sep 14. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010680.pub2
Casey S, Lanting S, Oldmeadow C, Chuter V. The reliability of the ankle brachial index: a systematic review. J Foot Ankle Res. 2019;12:39. Published 2019 Aug 2. doi:10.1186/s13047-019-0350-1
